What is CAD/CAM technology?
Digitalisation has revolutionised the delivery of dental treatments – leading to more predictable and faster outcomes while raising standards in the safety of each and every procedure.
CAD/CAM technology (computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing) represents some of the most advanced tools that exist in dentistry today to revolutionise any dental practice.
CAD/CAM technology is a digital workflow to fabricate restorations.
For dentists, CAD/CAM technology:
- Enhances the view of the oral cavity via a digital scan
- Creates 3D digital imaging
- Creates the design contours, occlusion and colour of restorations
- Plays a key role in the digital planning, design and manufacturing of restorations
- Saves space because digital scans take up less space than traditional models.
For patients, CAD/CAM technology:
- Provides an important patient communication tool
- Has the capacity to improve treatment uptake
- Does away with messy impressions
- Eradicates the need for temporary restorations
- Improves the patient experience
- Reduces chair time.
For lab technicians, CAD/CAM technology:
- Raises the bar in the fabrication of high-quality dental restorations in both function and aesthetics
- Simplifies communication between practice and laboratory
- Maximises efficiency
- Makes restoration fabrication more predictable
- Shape or mill restorations from CAD/CAM blocks created digitally
- Has the potential to be faster than traditional methods for producing indirect restorations
- Can deliver same-day restorations
- Can fabricate all types of restorations, including:
– Dentures
– Ceramic crowns
– Inlays and onlays
– Veneers
– Bridges
– Dental implants
– Full mouth reconstructions
– Orthodontics
– Removable prosthodontics.
While there is often a steep learning curve when incorporating CAD/CAM technology into everyday practice, once implemented and with proper training, CAD/CAM technology can be easy to use and offer quality comparable to traditional techniques.
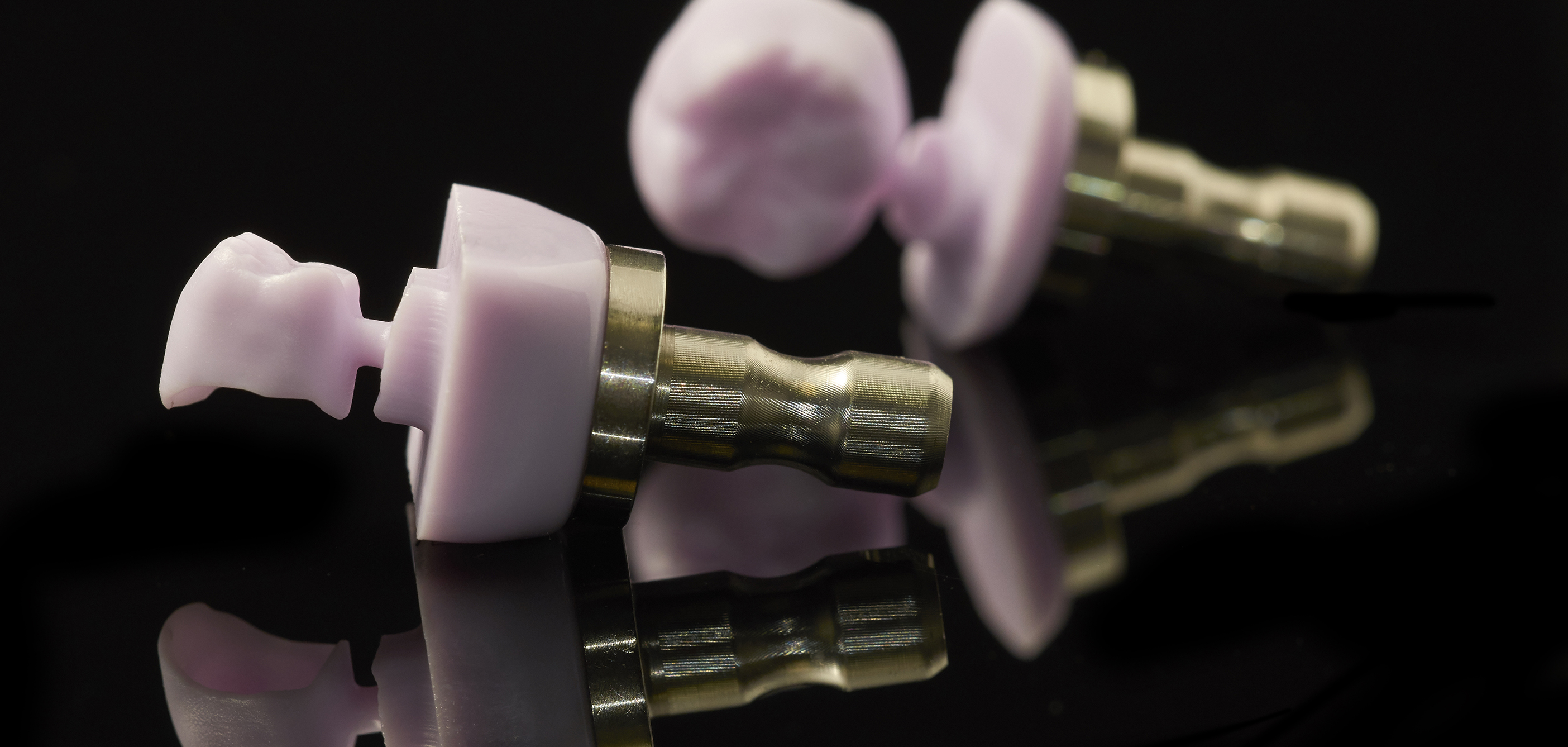
What are the different types of CAD/CAM Blocks?
CAD/CAM technology is renowned for its use of quality materials. The digital revolution brought with it some incredible opportunities in the choice of materials ¬– chairside as well as in lab-produced restorations.
CAD/CAM restorations create a natural appearance, because of the blocks used closely resemblance enamel and, once adapted, can blend seamlessly in the mouth even as natural-looking replacements for posterior teeth. CAD/CAM technology produces dental restorations in a variety of shades, sizes and colours.
The myriad high-performance CAD/CAM restorative materials that are available in a multitude sof hades and translucency can create restorations to blend perfectly with the mouth of each and every patient as well as meet clinical expectations.
Many manufacturers produce blocks of machinable ceramics or machinable composites. These materials are produced under ideal industrial conditions so that their physical properties have been fully optimised.
CAD/CAM blocks are capable of fabricating restorations with optical and physical characteristics similar to that of the tooth structure. By reproducing the natural elements of translucency, colour intensity and strength, CAD/CAM blocks help to integrate restorations in the remaining dentition.
The different types of blocks CAD/CAM blocks are:
- Zirconia Blocks. The material of choice for posterior teeth, these blocks have similar mechanical properties to those of stainless steel, which makes them strong and tough and incredibly durable. Their popularity is thanks to their biocompatibility, hardness, fracture resistance, durability and aesthetics. High-strength Zirconia is used for crowns, fixed partial dentures, posts and cores, implants and implant abutments.
- Lithium Silicate Glass Ceramic Blocks. These have adequate strength properties and are ideal solutions for all restorations. More translucent than Zirconia Blocks, their optical properties of these blocks support highly aesthetic indications. They adapt well to blend with remaining tooth structure and can be individualised using staining technique.
- Hybrid Ceramic Blocks. These feature a dominant ceramic network strengthened by a polymer network. Fully integrated, they offer a high degree of elasticity while guaranteeing high load capacity after adhesive bonding. This material is indicated for inlays, onlays and crowns.
- Multi Blocks. These offer a lifelike transition of shade, translucency and fluorescence and are suitable for anterior and posterior crowns and veneers as well as all-ceramic inlays and onlays. They can be polished or stained and glazed.
- Aesthetic Composite Blocks. These are used for the efficient fabrication of indirect single-tooth restorations. They blend in with the residual tooth structure to create pleasing aesthetic result quickly and easily.
- Resin Nano Ceramic Blocks. Less brittle than glass ceramic, these blocks are tough and resilient and help to achieve better edge quality and smooth margins for inlays and onlays that look and feel natural. Their precision and speed make them ideal for single-appointment efficiency.
- Nano Hybrid Composite Blocks. These resemble natural teeth perfectly with elasticity and surface hardness identical to natural tooth substance. With high flexural strength, they are ideal for grinding even in cases with thin margins.
Which CAD/CAM Block should I use?
When selecting a block, it is important to make sure it is suitable for the intended restorative indication. Different blocks require different protocols and procedures and have different properties. Some are best suited to posterior restorations, while others have less of an emphasis on strength and durability and focus on natural aesthetic results required for anterior work.
Blocks can be monochromatic porcelain, which is uniform throughout and therefore requires the clinician to match shades, translucency and characteristics, which can be challenging. On the other hand, polychromatic blocks aid in the shade matching process, although clinicians can work with these to characterise, glaze and make further shade adjustments.
Blocks with low translucency – similar to that of natural dentin – are best suited for creating large restorations, such as posterior crowns. With their natural likeness in brightness, colour and shade, other blocks are better suited to anterior restorations because they are designed to blend seamlessly with existing teeth.
The ever-developing range of CAD/CAM block options offers dentist opportunities to tailor their choices of material to best meet the expectations of each and every patient.
Which CAD/CAM Block is the best?There have been some amazing advancements in the development of materials used to fabricate restorations – in strength, in durability, in aesthetics, flexibility and in ease of use.
While Zirconia and Lithium Silicate remain popular choices for restorations, the new generation of CAD/CAM restorative materials are continually being developed in a bid to improve mechanical integrity and enhance translucency and longevity.
Good clinical outcomes of any restoration lie not solely in the unique physical properties of each CAD/CAM block, but also in its applications as well.
Handled correctly, resilient CAD/CAM materials offer the best in long-lasting, functional and aesthetically appealing restorations.